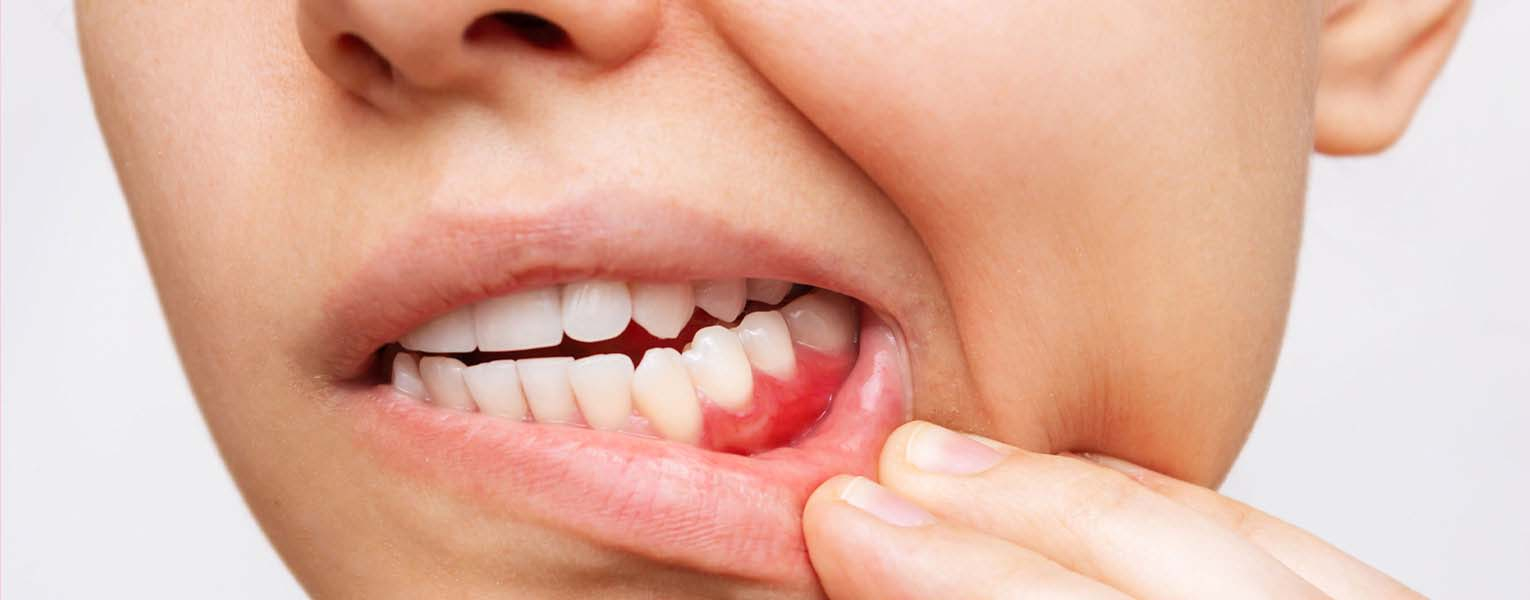
What is Gum Bleeding and Why Does it Occur?
Gum bleeding refers to the leakage of blood elements outside of the vessels due to the disruption of the structure of the vessels that nourish the gum tissue, which develops due to the presence of attachments such as plaque and calculus on the tooth surface associated with gum disease. In other words, bleeding gums are the initial sign of inflammatory gum disease. This bleeding can occur in response to stimuli (touching, brushing, etc.) or spontaneously. In addition to this, factors such as vigorous brushing, protruding or poorly done fillings, cavities, and ill-fitting prostheses can also cause bleeding. Pregnancy, menstruation, menopause, blood disorders, diabetes, deficiencies in vitamins C and K, genetic predisposition, and the use of blood thinning medications can also manifest as gum bleeding.
How is Gum Bleeding Treated?
Gum bleeding is treated by diagnosing the causative factor and implementing appropriate measures. This includes scaling and root planing if necessary, along with plaque removal. Proper patient care is crucial during the healing process. Therefore, proper brushing and the use of dental floss or interdental brushes should be included as necessary. If there are cavities present, they should be treated, and ill-fitting fillings or prostheses should be corrected or replaced. Any systemic problems that may cause bleeding should be identified and discussed with the patient's physician.
Article by: Dr. Ece Akkan